

ĭisorders of hormone over/under-production

Scientist Eugene Merle Shoemaker, co-discoverer of the Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 had Addison's Disease.
Some have suggested Jane Austen was an avant la lettre case of Addison's Disease, but others have disputed this.Kennedy, the 35th president of the United States was diagnosed with Addison’s disease. Notable people with adrenal gland disorders Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia, a family of syndromes in which genetic abnormalities contribute to the development of endocrine tumors.Von Hippel–Lindau disease, a mutation of the VHL1 tumor-suppression gene associated with many types of tumor, including pheochromocytoma.Hereditary disorders associated with adrenal tumors Pheochromocytoma, a catecholamine-producing tumor of the adrenal medulla, which may or may not be cancerous.Adrenal incidentaloma, an adrenal tumor (of any type) discovered accidentally during a scan which performed for an unrelated reason.Adrenocortical carcinoma, cancer of the adrenal cortex.Adrenal adenoma, a benign tumor of the adrenal gland which may result in overproduction of one or more adrenal hormones, or may be inactive.

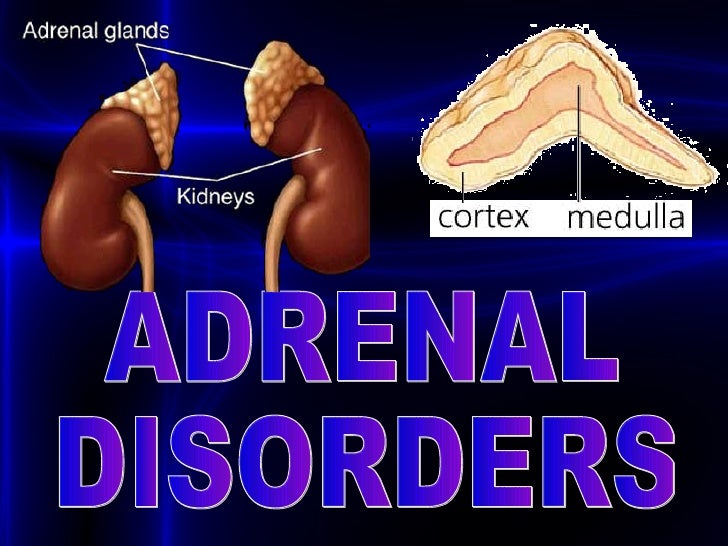
Disorders of the adrenal gland may affect the production of one or more of these hormones. The adrenal medulla produces epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline). The adrenal cortex produces mineralocorticoids, which regulate salt and water balance within the body, glucocorticoids (including cortisol) which have a wide number of roles within the body, and androgens, hormones with testosterone-like function. There are two parts of the adrenal glands, the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. The adrenal gland produces hormones that affects growth, development and stress, and also helps to regulate kidney function. Adrenal disorders may cause hyperfunction or hypofunction, and may be congenital or acquired. Adrenal gland disorders (or diseases) are conditions that interfere with the normal functioning of the adrenal glands.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
